Inside ExoMars - Quarterly Newsletter
Issue 6 - February 2012
| What’s new for this quarter: | |
| - |
Successful reviews for the preliminary design of the Orbiter spacecraft and several EDM subsystems will enable the start of their detailed design. |
| - |
The materials for the Orbiter central tube flight model were ordered. |
| - |
First full scale tests for mechanical systems of the 2016 spacecraft. |
| - |
The drill engineering qualification model was assembled and is ready to undergo test campaigns. |
Updates on payloads and spacecraft design
ESA has approved for the last quarter of 2011 the sufficient funding to continue the progress on critical subsystems, maintaining the launch dates in 2016 and 2018 respectively for the two missions within the ExoMars programme.
The Orbiter spacecraft and several EDM subsystems (Heat shield, propulsion system, surface platform structure, radar Doppler altimeter, and parachute) preliminary designs have been successfully reviewed, enabling the start of their detailed design.
Following the preliminary design review of the Orbiter central tube, which is the first important piece of the Orbiter’s hardware to be built, the materials for the manufacturing of its flight model were ordered by Astrium ECE in Madrid, Spain. Furthermore, the contracts for a number of avionic equipment and units were finalised.
In the meantime, a full scale model of the mechanism that will give the right separation velocity and spin rate to the EDM when released from the Orbiter, three days before reaching the atmosphere of Mars, was tested to verify this critical element in the success of the mission. A full scale model of the EDM surface platform was also constructed, by SENER in Spain, to test its crushable structure, which is designed to limit the landing shock and avoid damaging the lander equipment. Several tests are planned for the beginning of 2012 on a variety of representative Mars-like terrains and landing speeds at the CTA facilities in Vitoria, Spain.
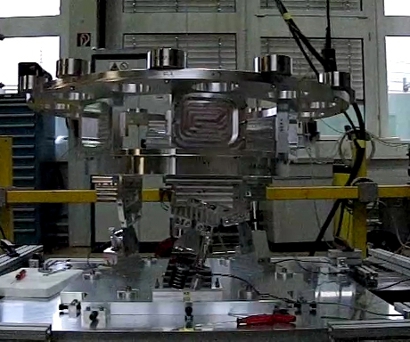 |
|
A full scale model of the mechanism that will give the right separation velocity and spin rate to the EDM when released from the Orbiter, three days before reaching the atmosphere of Mars. Credit: RUAG |
The activities for the DREAMS payload, the EDM science payload that will function as an environmental station for the duration of the mission on the surface Mars, are also progressing. The review on the preliminary design of the DREAMS payload will commence on 15 March.
In parallel to the study work on the Rover, the design and test activities are ongoing. These tests activities included a campaign on the Rover guidance, navigation and control system at ASU Mars Yard facilities in Stevenage, UK, as well as functional tests of engineering models of the sample handling and distribution system mechanisms (core sample transport mechanism, and powder sample dosing and distribution mechanism) in simulated Mars conditions at the Kayser-Threde facilities in Munich, Germany. Following the successful tests earlier last year, the drill engineering qualification model was assembled at Selex Galileo in Milano, Italy. A test campaign with the electronics engineering model and the first software version is planned for the first months of 2012.
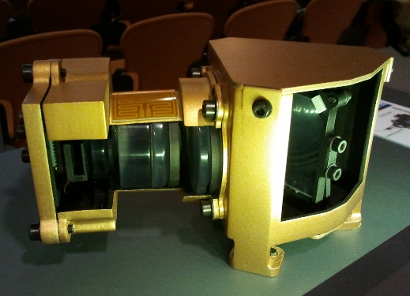 |
|
A mock-up of the ExoMars Raman Spectrometer, a powerful tool for the definitive identification and characterisation of minerals and biomarkers, during tests. |
The Rover instruments design and testing is also progressing. Recent tests of the ExoMars Raman Spectrometer mock-up demonstrated its design capabilities and new models of the other instruments are being built for tests in the following months.
|
Save the Date | ||
| 13-15 February California, U.S.A. |
Conference on Life Detection in Extraterrestrial Samples |
 |
| 27-28 February Virginia, U.S.A. |
2nd International Mars Exploration Program Analysis Group (MEPAG) meeting |
 |
| 29 February - 2 March Washington, U.S.A. |
Landing Site Workshop for Future Mars Missions |
 |
| 22-27 April Vienna, Austria |
European Geosciences Union, General Assembly 2012 |
 |
| 15-17 May California, U.S.A. |
Mars Recent Climate Change Workshop |
 |
| 21-25 May Nevada, U.S.A. |
3rd International Conference on Early Mars |
 |
| 14-22 July Mysore, India |
COSPAR 2012: 39th COSPAR Scientific Assembly and Associated Events |
 |
| 10-12 September Texas, U.S.A. |
The Mantle of Mars: Insights from Theory, Geophysics, High-Pressure Studies, and Meteorites |
 |
| 25-27 October Marrakech, Morocco |
3rd Conference on Terrestrial Mars Analogues |
 |
|
For more information, you can also access the complete Events Archive | ||
|
ExoMars Timeline | |
|
2011 | |
| October | Negotiations with the Russian Space Agency for a possible future collaboration |
| December |
Preliminary Design Review of the Trace Gas Orbiter - completed |
| April - December |
ESA-NASA Joint Exploration Working Group studies to establish an architecture for the joint single rover mission in 2018 |
|
2012 | |
| January | Study completion on the possible cooperation with the Russian Space Agency |
| March |
Preliminary Design Review of the DREAMS payload - kick off |
| March – April |
Mission concept review concluding on the joint Rover architecture |
|
For more information, you can also access the complete ExoMars timeline Disclaimer: Future milestones are indicative and subject to change | |
To stay informed about the ExoMars activities, subscribe to our mailing list.
| ESA – ExoMars Programme | Don McCoy |
RoboticExploration esa.int esa.int |
ExoMars Project Manager |
